differential scanning calorimetry principle
Search for more papers by this author. The method allows you to identify and characterise materials.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Search for more papers by this author.
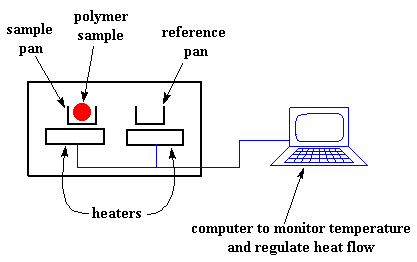
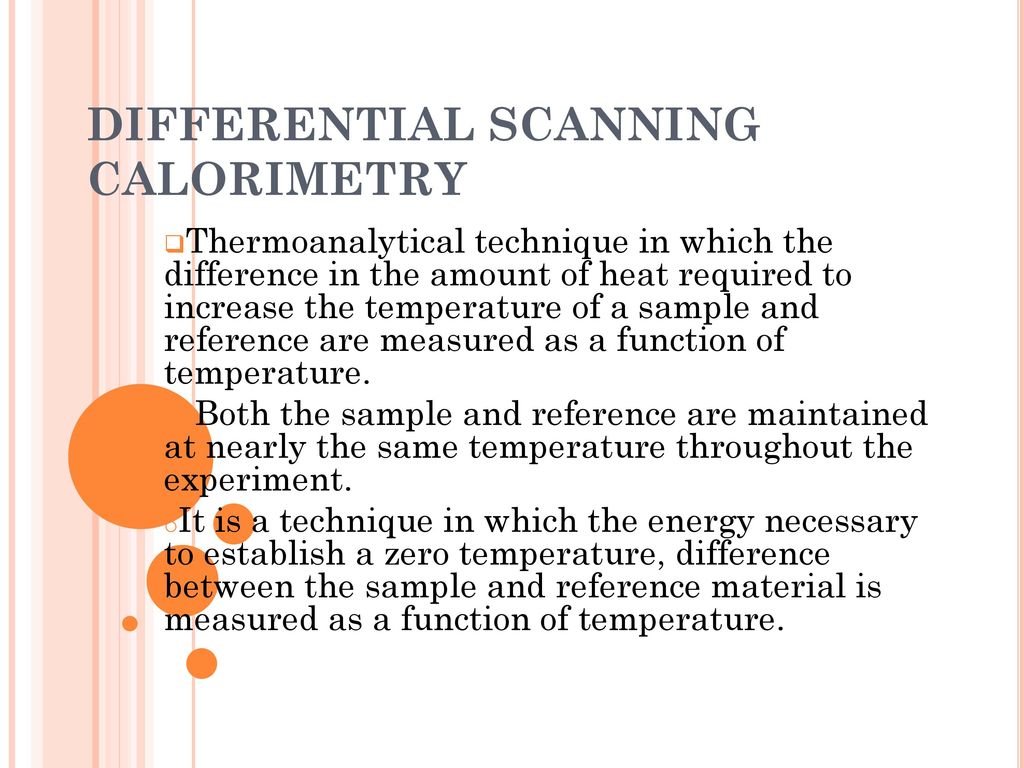
. A calorimeter measures the heat into or out of a sample. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. 18 September 2015.
Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is one of the thermo-analytical techniques. The method allows you to identify and characterize materials. A technique for the relationship between the power difference and.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry 31 Introduction Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is an experimental technique for measuring the. This allows the detection of transitions such as melts. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of.
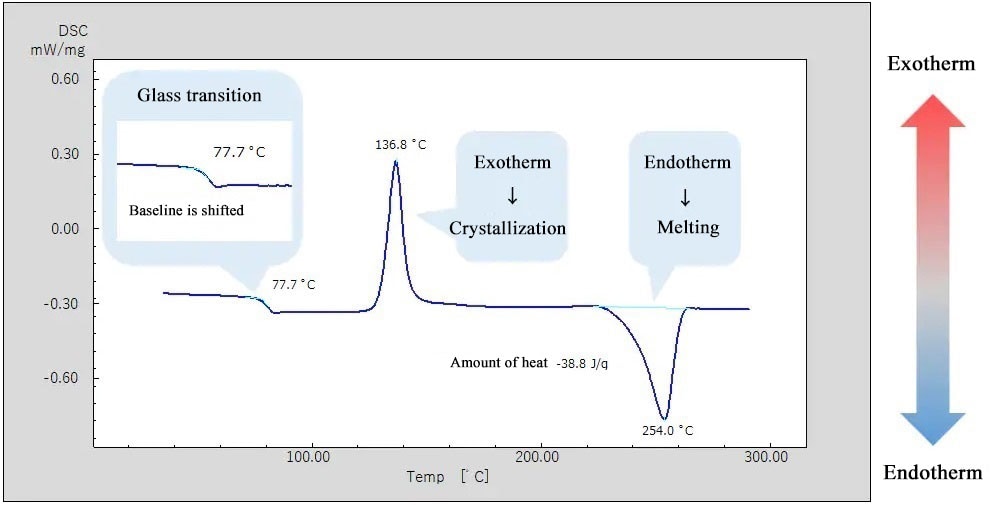
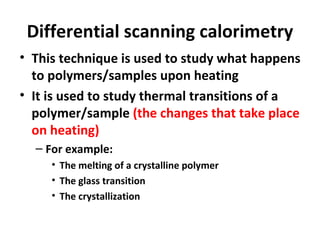
The basic principle underlying this technique is that when the sample undergoes a physical transformation such as phase transitions more or less heat will need to flow to it than the reference to maintain both at the same temperature. DSC is used to measure enthalpy changes due to changes in the physical and chemical properties of a material as a function of temperature or time. The basic principle underlying.
A differential scanning calorimeter does all of the above and heats the sample with a linear temperature ramp 3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Basic Theory Applications Training DSC DSC Training Course Agenda Understanding DSC Experimental Design. Principles of DSC and types of measurements made.
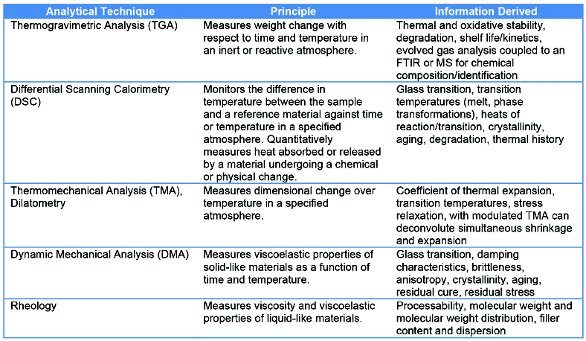
A sample of known mass is heated or cooled and the changes in its heat capacity are tracked as changes in the heat flow. DSC measures enthalpy changes in samples due to changes in their physical and chemical properties as a function of temperature or time. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is the most frequently used thermal analysis technique alongside TGA TMA and DMA.
For example as a solid sample melts to a liquid it will require more heat flowing to the sample to increase its temperatur. The principle of the DTA technique resumes to heating or cooling a test sample S and an inert reference R under identical conditions while measuring the temperature. A constant heating rate is overlapped by a further modulated temperature control.
The sinusoidal temperature perturbation leads to a resulting sinusoidal. 422331 Differential scanning calorimetry. Differential Scanning Calorimetry We must understand that the principle of this calorimeter is actually differential scanning calorimetryDifferential Scanning Calorimetry DSC measures the input material and reference material under the control of the program temperature.
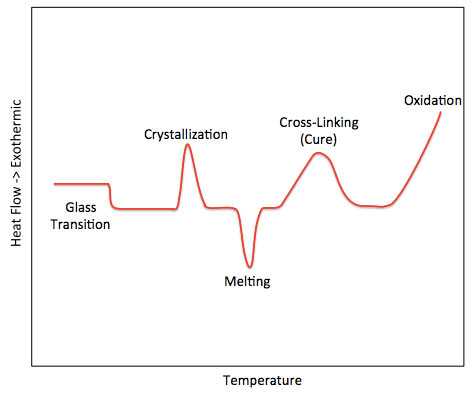
A differential calorimeter measures the heat of sample relative to a reference. In case of DSC. The DSC principle is based on the fact that under constant pressure conditions the.
Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is the most frequently used thermal analysis technique. Both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the experiment. DSC is used to measure enthalpy changes due to changes in the physical and chemical properties of a material as a function of temperature or time.
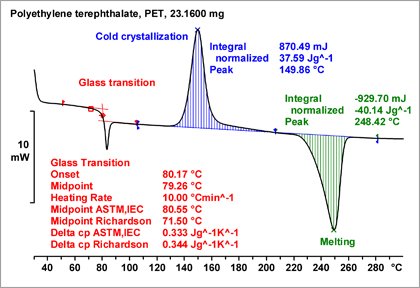
DSC Differential Scanning Calorimetry Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is one of the thermalanalysis techniques. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a Thermo-analytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a technique that can be used to determine phase transition temperatures Tg Tm and heat capacities Cp of the analyzed samples.
The samples are loaded into a pan of known dimensions hermetically sealed in some cases and heated at a fixed rate C min. Principle To maintain the sample and reference at equal temperature during the physical transformations of the sample like phase transitions either more or lesser amount of heat is required to be. The DSC utilizes an innovative DSC sensor with 120 thermocouples which guarantees unbeatable sensitivity and.
Temperature Modulated Differential Scanning Calorimetry TM-DSC is a DSC technique whereby a sample is subjected to a superposition of a linear and a periodic temperature program. A Practical Introduction to Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Differential scanning calorimetry Principle.
A Differential Scanning Calorimetry or DSC is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a materials heat capacity Cp is changed by temperature. Calorimetry is a primary technique for measuring the thermal properties of materials to establish a connection between temperature and specific physical properties of substances and is the only method for direct determination of the enthalpy associated with the process of interest. DSC Differential Scanning Calorimetry is a technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference are measured as a function of temperature.
Whether less or more heat must flow to the sample depends on whether the process is exothermic or endothermic. Learn about the principles of Differential Scanning Calorimetry DSCDifferential Scanning Calorimetry DSC is a technique for understanding the stability o. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is the most frequently used thermal analysis technique alongside TGA TMA and DMA.
Expanded Principle of Operation Q Ts -Tr A B C R Thermal Resistance Imbalance Thermal Capacitance Imbalance Heating Rate Imbalance Tfs Ts Rs Tfr Tr Rr Cs. 1 2 Calorimeters are used frequently in chemistry 3 biochemistry 4 5 cell. The sample and reference material are maintained at the same.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Ppt Download
Chapter 2 What Is A Dsc Shimadzu Shimadzu Corporation

Principle Of Differential Thermal Analysis Dta Hitachi High Tech Global

Differential Scanning Calorimetry How Does It Work

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Online Training Course Youtube
Dsc Analysis Fundamentals And Applications

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Eindhoven University Of Technology Research Portal
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc As An Analytical Tool In Plastics Failure Analysis American Laboratory

Principle Of Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Download Scientific Diagram
Differential Scanning Calorimetry A Review Open Access Journals

M6 Differential Scanning Calorimetry Review Of Operating Principles And Applications In Themal Anal Youtube
Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Principle Of Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Hitachi High Tech Global

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Principle Instrumentation Application Of Dsc Youtube
Differential Scanning Calorimetry A Review Open Access Journals

Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Differential Scanning Calorimetry An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Based Analysis Service Creative Proteomics
No comments for "differential scanning calorimetry principle"
Post a Comment